#Who is the strongest ‘working AI’? OpenAI personally tested it, but the first result was not oneself
OpenAI released its latest research, but praised Claude in it.
They proposed a new benchmark called * * G * * * DPval * * to measure the performance of AI models on real-world tasks with economic value.
Specifically, GDPval covers 44 professions in the top 9 industries that contribute the most to US GDP, with a combined annual revenue of $3 trillion. The task is designed based on representative work of industry experts with an average of 14 years of experience.
Professional assessors compared the output results of mainstream models with the achievements of human experts.
In the final test, Claude Opus 4.1 became the best performing model, with 47.6% of the output rated as comparable to that of human experts.
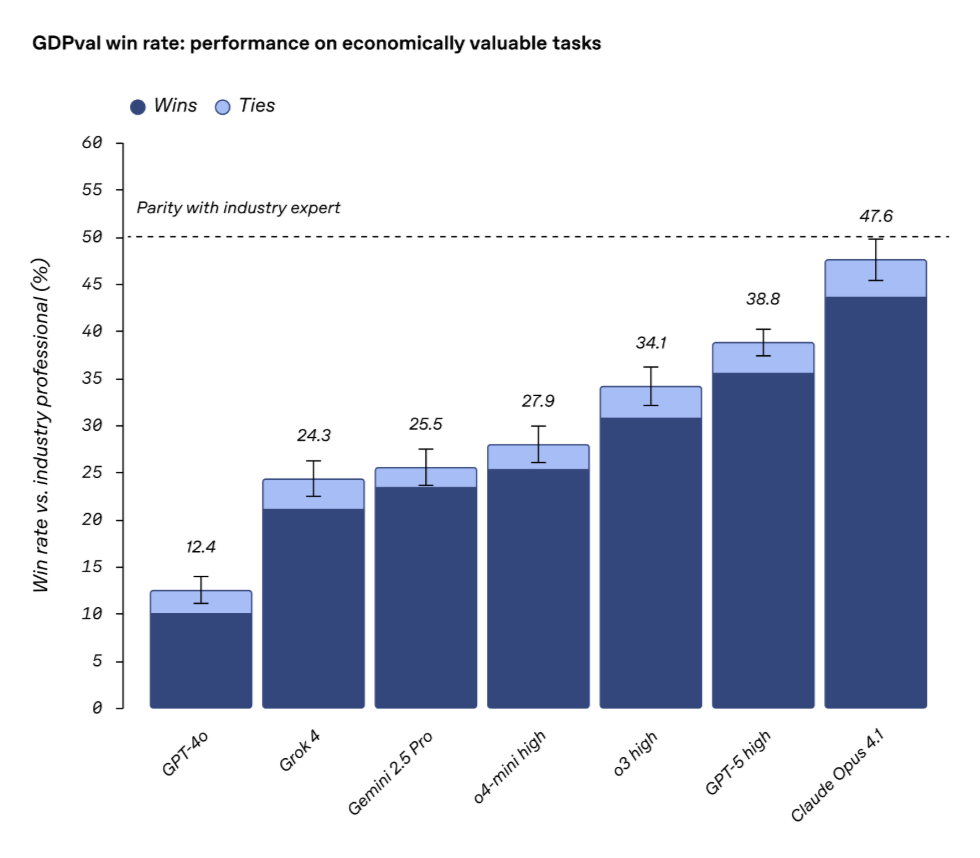
GPT-5’s score of 38.8% is still slightly behind Claude’s, ranking second; GPT-4o has only 12.4% wins or draws compared to humans.
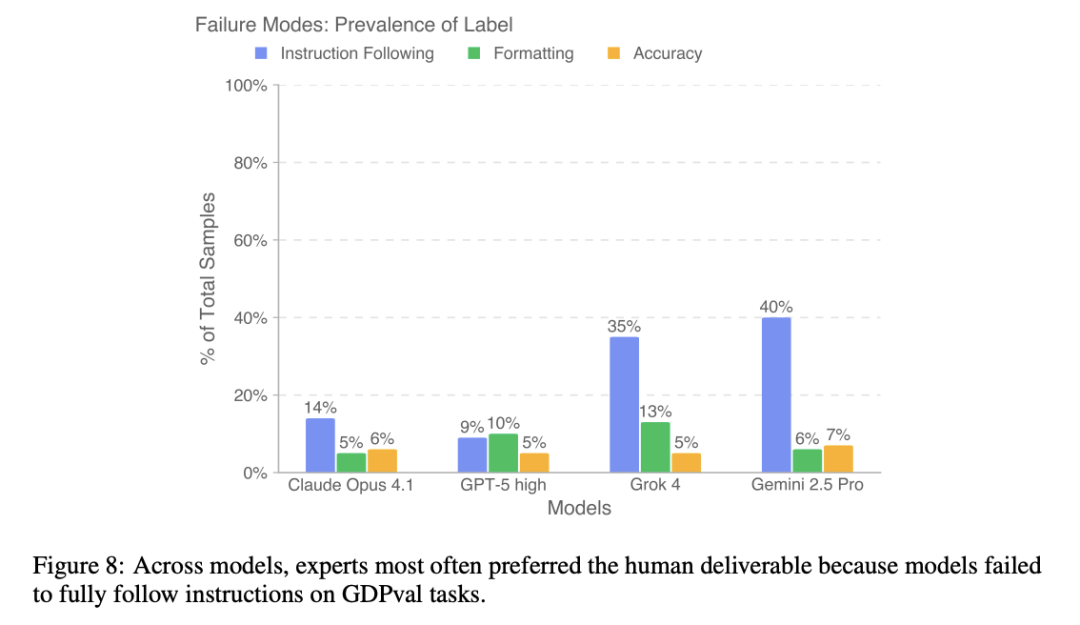
Unable to become the best, OpenAI also made up for itself: different models have their own advantages, Claude Opus 4.1 is mainly outstanding in aesthetics, while GPT-5 is better in accuracy.
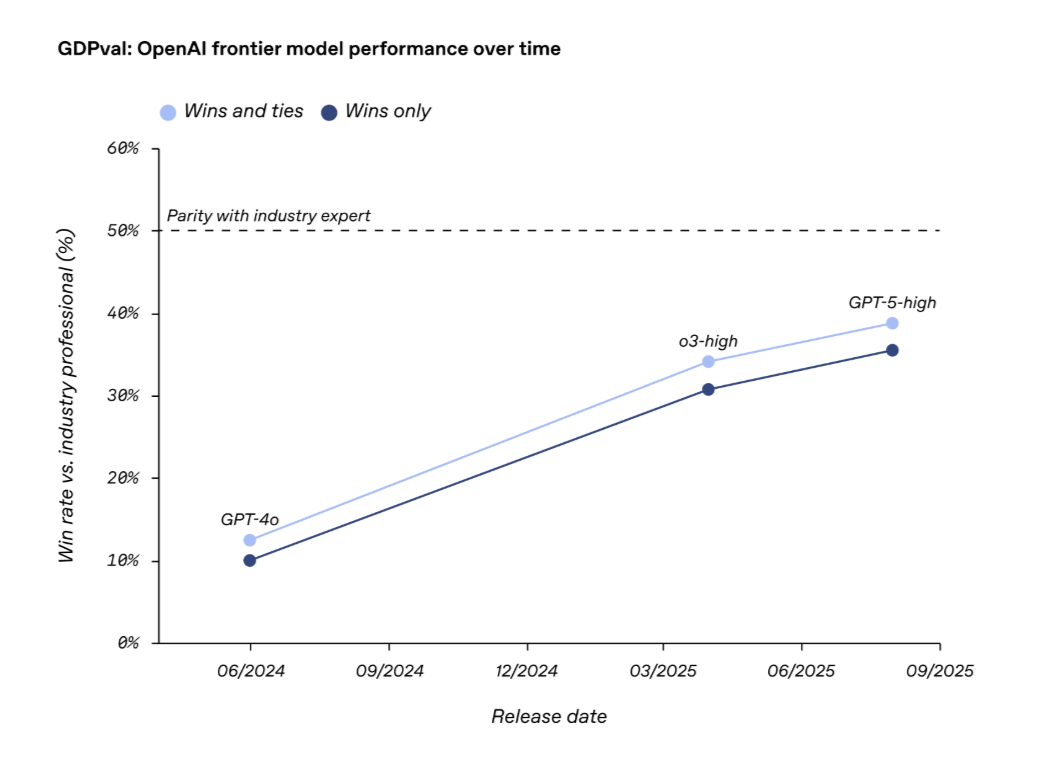
OpenAI also stated that it is worth noting the speed of model progress, with its cutting-edge models almost doubling their win rate in just one year.
Finally, OpenAI also open sourced a high-quality subset of 220 tasks and provided a publicly available automatic rating service.

After watching it, netizens expressed that they were very impressed by Sting’s research:
The performance of OpenAI’s various models has shown linear growth, and we are grateful for the recognition of our competitors.

Some netizens also believe that this may be a carefully designed promotional tactic by Ultraman, raising funds by boasting that AI can bring growth to GDP.
Let’s take a closer look at this test.
##Testing AI’s ability to make money
OpenAI points out that compared to existing AI evaluations, the advantage of GDPval is that:
+The task is based on real work results and is associated with completion time and cost, with practicality;
+Covering most of the occupational work activities tracked by O * NET (American Occupational Information Network), with representative breadth;
+The task requires processing multiple format files and parsing multiple reference files, involving computer usage and multimodality;
+In addition to correctness, subjective factors such as structure and style also need to be considered. The dataset can also serve as a testing platform for evaluating the performance of automatic scoring systems;
+The winning rate as the main indicator has no upper limit and supports continuous evaluation;
+The task difficulty is high, with industry professionals taking an average of 7 hours to complete, and complex tasks can even take several weeks.
The task construction process starts with determining the core industry and profession.
OpenAI first screened out 9 industries that contribute over 5% to the US GDP (based on the percentage of added value of each industry to the US GDP in Q2 2024), and then selected 5 professions with the highest contribution to total wages and mainly focused on digital tasks within each industry.
When determining whether a profession is “primarily focused on numerical tasks”, refer to all tasks in O * NET for that profession, use GPT-4o to classify tasks according to “numerical/non numerical”, and weight the relevance, importance, and frequency scores of tasks in O * NET. If more than 60% of tasks are numerical tasks, the profession will be included.
Ultimately, OpenAI identified 44 professions with a combined annual revenue of $3 trillion.

Continuing with the recruitment of industry professionals, it is required that experts involved in task creation have at least 4 years of relevant professional experience, and their resumes should reflect professional recognition, promotion experience, and management responsibilities.
According to statistics, the recruited industry experts have an average of 14 years of experience.
These individuals need to undergo further video interviews, background checks, training, and testing to participate in the project (OpenAI will also offer a generous compensation), and their former employers include Apple, Google, Microsoft Meta、 Samsung, Oracle IBM、 Morgan Stanley and many other well-known enterprises and institutions ensure that experts have a solid foundation in industry practice.
In the task creation process, each GDPval task consists of two parts: “requirements” and “deliverables”. Industry experts will classify and design tasks based on their own profession in O * NET to ensure the breadth and representativeness of task coverage.

In order to evaluate the quality of tasks, OpenAI requires these experts to rate the difficulty, representativeness, completion time, and overall quality of each task based on the actual standards of their profession, and to calculate the economic value of each task by combining the median hourly wage of the corresponding profession in OEWS (Bureau of Labor Statistics Occupational Employment Statistics) data through “average completion time x hourly wage”.
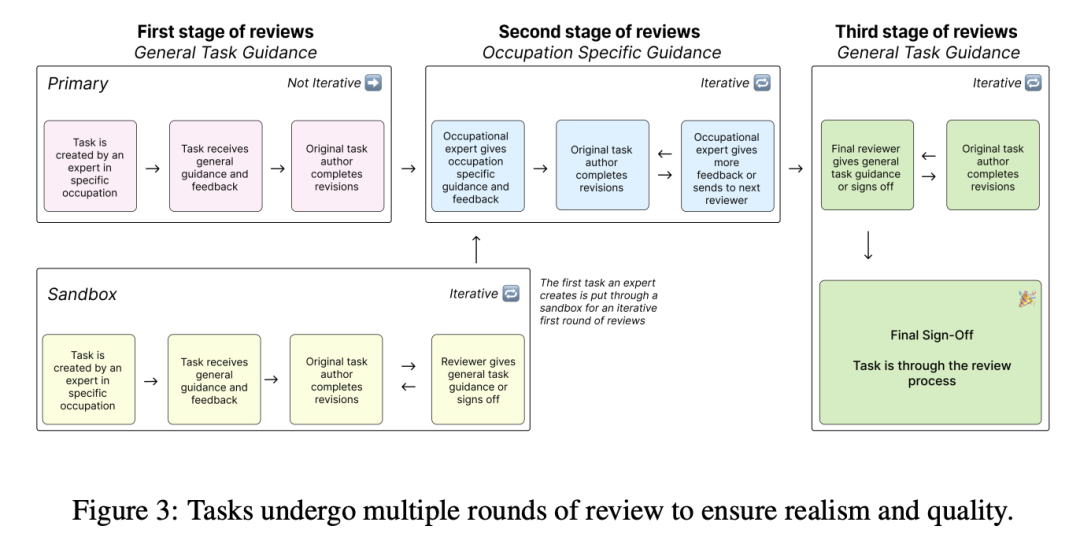
In the end, the GDPval dataset contained a total of 1320 tasks, all of which underwent an iterative process of “automated model screening+multiple rounds of human expert review”, with each task receiving at least 3 manual reviews, averaging 5 reviews.
Experts will provide detailed opinions at each review stage. The task will be repeatedly revised and improved based on feedback.
##Claude’s performance rivals that of human experts
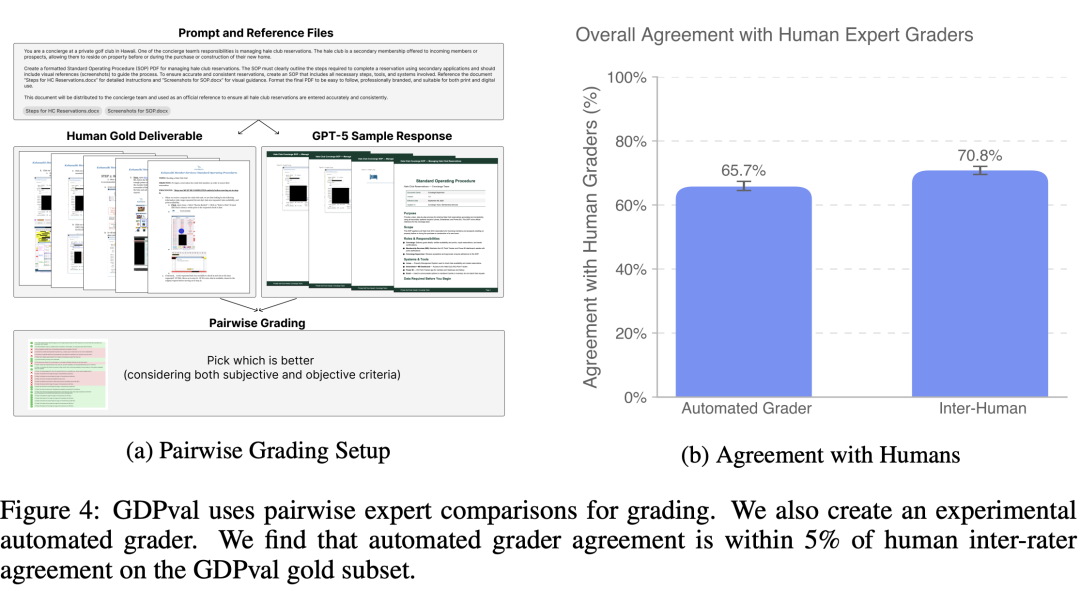
OpenAI has open sourced a high-quality subset of 220 tasks and used blind expert pairwise comparison method (i.e., a pairwise comparison scoring method where experts do not know the source of the evaluated results) to rate the subset.
The average time for each comparative rating exceeds 1 hour. OpenAI has also invited more experts in various professional fields to rate the results of human experts and model outputs. Experts need to provide detailed basis for their selection and ranking results.
OpenAI has also developed an experimental automatic scoring system for high-quality subsets, which has a consistency rate of 66% with human expert ratings, only 5% lower than the consistency rate between human ratings (71%).
After evaluating the GPT-4o, o4 mini, o3, GPT-5, Claude Opus 4.1, Gemini 2.5 Pro, and Grok 4 models, the results showed that:
In the high-quality subset task of GDPval, Claude Opus 4.1 is the model with the best overall performance, especially in terms of aesthetics such as document format and slide layout.
Among its output results, 47.6% were rated as better than or equivalent to the level of human experts.
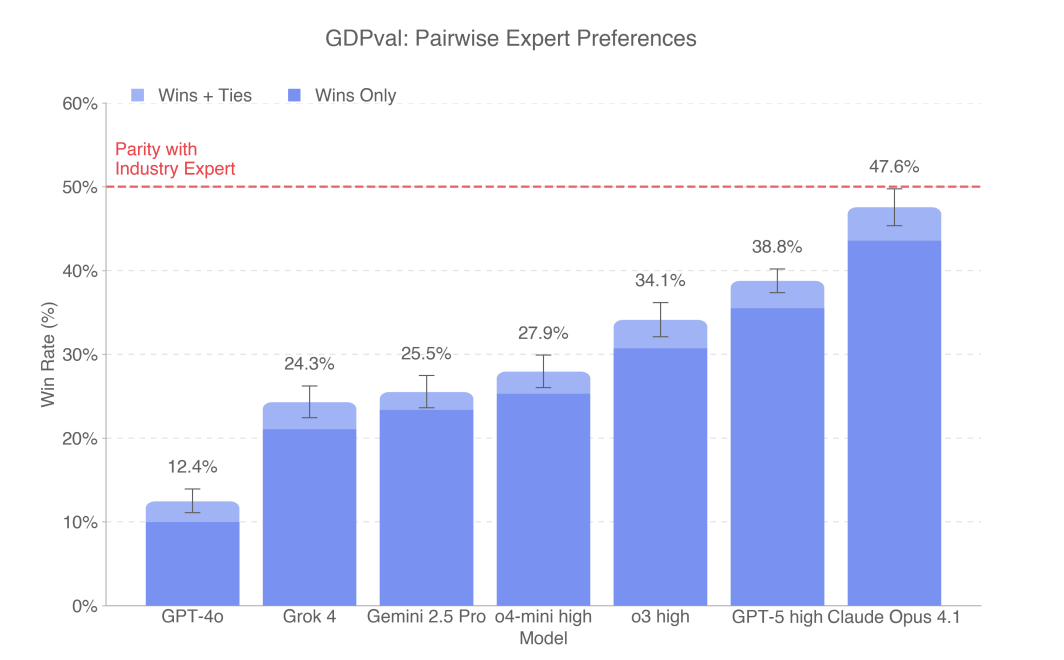
The performance of OpenAI’s various models on GDPval shows a roughly linear improvement.
According to the figure below, GPT-5 has significant advantages in accuracy, such as strictly following instructions and completing correct calculations.
In other words, GPT-5 performs better on plain text tasks, but Claude performs better on file types such as. pdf,. xlsx, and. ppt, demonstrating stronger visual perception and aesthetic design abilities.
Among all tasks in the high-quality subset of GDPval, slightly more than 50% of the tasks have at least one model with output results that are superior to or comparable to human experts.
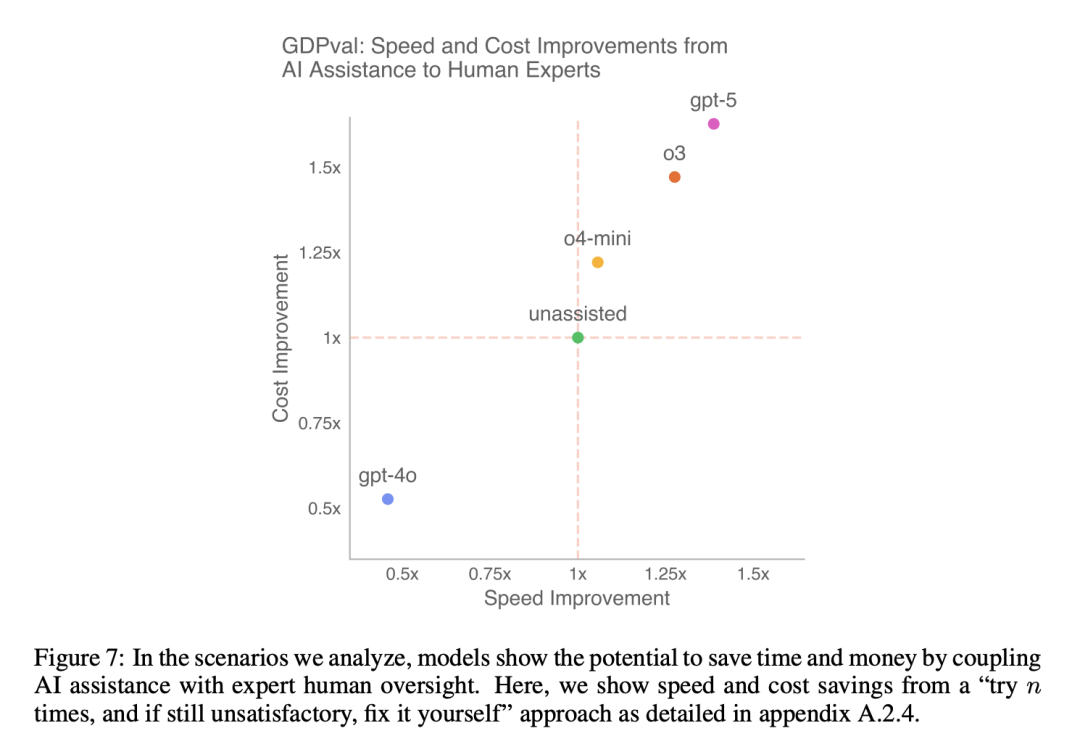
OpenAI also pointed out that combining AI models with human supervision is expected to be more cost-effective than relying solely on human experts to complete tasks.
Whether it is the mode of “letting the model try first and then making changes if not satisfied” or the mode of “directly using the model results” or “only letting the model try once and then making it yourself”, both can help humans save costs and time.
In addition, research has found that increasing inference effort (such as setting different inference strengths for o3 and GPT-5), providing more task backgrounds, optimizing prompt words and agent assisted frameworks (such as supporting GET requests in containers, using the “N=4” “optimal N-to-1” sampling strategy, and using GPT-5 as the judgment model) can significantly improve model performance.
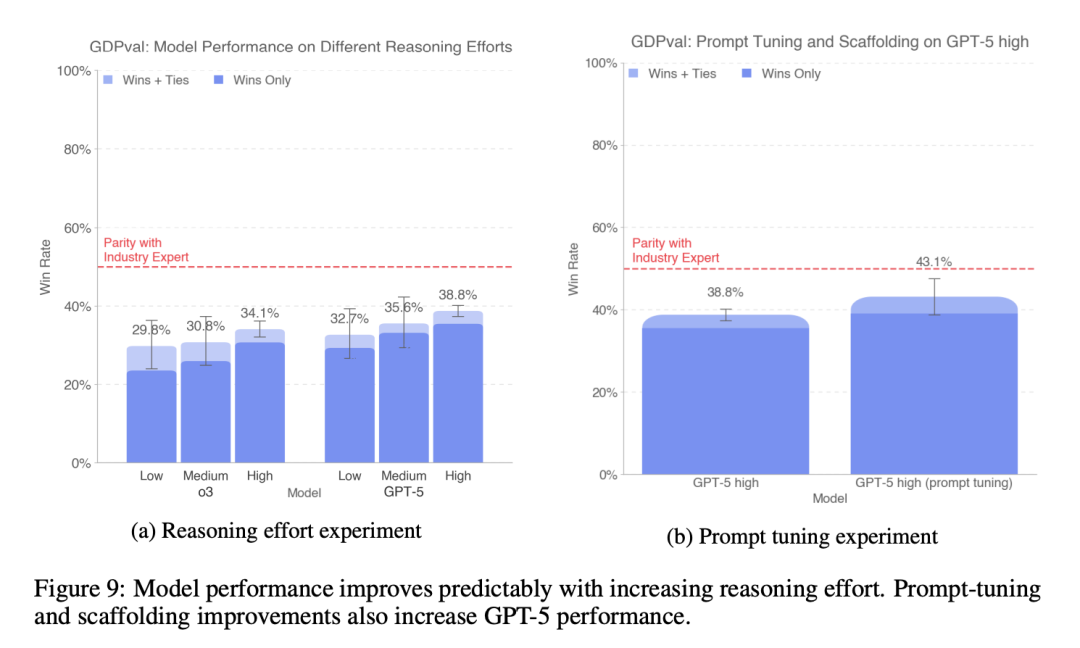
OpenAI also pointed out the limitations of GDPval, such as limited dataset size (only 44 professions), focus on knowledge work that can be completed on computers (excluding physical labor, etc.), one-time tasks that are precisely specified (lack interactivity), shortcomings of automatic scorers, and high evaluation costs.
At present, GDPval is still in its initial stage, and OpenAI plans to gradually expand its coverage, enhance realism and interactivity, and incorporate more scene details in future iterative versions.

By the way, Not only OpenAI thinks Claude is good, but also former close ally Microsoft recently received news that they will work together with Anthropic to optimize Microsoft 365 Copilot AI Assistant (doge).
Reference link:
*[1] https://x.com/OpenAI/status/1971249374077518226 *
*[2] https://evals.openai.com/ *
